In recent years, fueled by consumers’ growing demand for low-calorie diets, sweetness-related keywords such as “low-sugar” and “zero-sugar” remain highly popular. Sugar substitutes are widely used in the downstream food and beverage industry, due to the characteristics of high-sweet, low-calorie, and not causing a rise in blood sugar levels.
Steviol glycosides is a high-sweet, low-calorie natural sweetener extracted from stevia. Currently approved for use in food in China, the EU, the United States, Australia, New Zealand, Canada, and other countries/regions, it is hailed as the world’s third-generation natural zero-calorie healthy sugar source.
Steviol glycosides are composed of various glycosides. According to the National Food Safety Standard for Food Additives - Steviol Glycosides (GB 1886.355-2022) implemented by the China National Health Commission (NHC) in 2022, known glycosides in China include stevioside, Rebaudioside A, B, C, D, E, F, M, N, O, Dulcoside A, Rubusoside, and Steviolbioside.
Since the sweetness levels of glycosides vary, an increasing number of enterprises globally are applying for individual glycosides to meet the diverse market demands, with the application of rebaudioside being the most popular. Primarily extracted from the leaves of the stevia plant, steviol glycosides and rebaudioside A present at the highest level in stevia and have a subtle bitter and lingering taste profile despite the relatively mature production process. Rebaudioside D and rebaudioside M present at very low levels in the stevia leaf, which has a taste profile that is more reflective of sucrose due to the high sweetness and pure taste when compared to the major glycosides. However, the traditional plant extraction method used for their preparation not only incurs high costs but also struggles to meet market demand. Currently, they are mainly prepared through microbial conversion or enzymatic synthesis methods.
CIRS has summarized the approval information of steviol glycosides and rebaudioside in the EU and the United States in the following.
EU
In 2011, E 960 (steviol glycosides) was included in Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 on food additives, and steviol glycosides were authorized to be used as a sweetener in food and beverages in the EU market.
In 2021, Commission Regulation (EU) 2021/1156 was released, authorizing the use of enzymatically produced rebaudioside as a sweetener. In the interest of clarity, the entry for “E 960 (Steviol glycosides)” is replaced by “E 960a (Steviol glycosides from Stevia)” and “E 960c (Enzymatically produced steviol glycosides)”.
In 2022, (EU) 2022/1922 was released, amending the above-mentioned regulations and inserting the following entries after the Enzymatically produced steviol glycosides (E 960c): Rebaudioside M produced via enzyme modification of Steviol glycosides from stevia (E 960c (i)), Rebaudioside M produced via enzymatic conversion of highly purified Rebaudioside A stevia leaf extracts (E 960c (ii)), Rebaudioside D produced via enzymatic conversion of highly purified Rebaudioside A stevia leaf extracts (E 960c (iii)), and Rebaudioside AM produced via enzymatic conversion of highly purified stevioside stevia leaf extracts (E 960c (iv)).
In 2023, Commission Regulation (EU) 2023/447 was released, amending the above-mentioned regulations and inserting the entry of Glucosylated steviol glycosides (E960d).
The current specifications stipulate that steviol glycosides (E 960) are to contain not less than 95 % of eleven named steviol glycosides: stevioside, rubusoside, dulcoside A, steviolbioside and rebaudiosides A, B, C, D, E, F and M.
It’s worth noticing that steviol glycosides are classified and managed as a food additive instead of a novel Food in the EU*.
* Novel Food refers to food that wasn’t widely consumed in the EU before May 15, 1997, including newly developed innovative foods, those produced using new technologies or processes, and traditional foods from a third country. If an enterprise plans to place products containing novel food on the EU market, it must undergo the novel food application process, a pre-market evaluation procedure.
U.S.
Based on the inventory of FDA GRAS notices, CIRS has made a thorough summary of the approved steviol glycosides and rebaudiosides and analyzed them from multiple perspectives (see Table 1).
Overall approval status
Since 2008, over 70 steviol glycosides and rebaudiosides have been granted GRAS approval. Approved rebaudiosides include Rebaudioside A, B, C, D, E, M, and I.
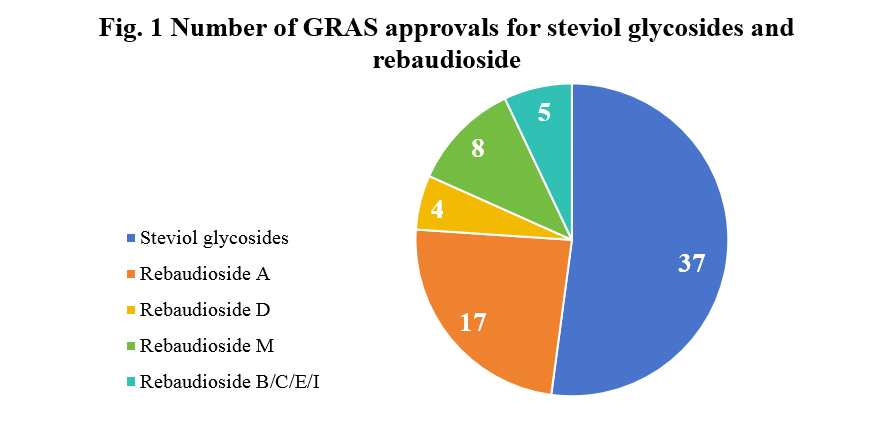
Number of approvals by countries
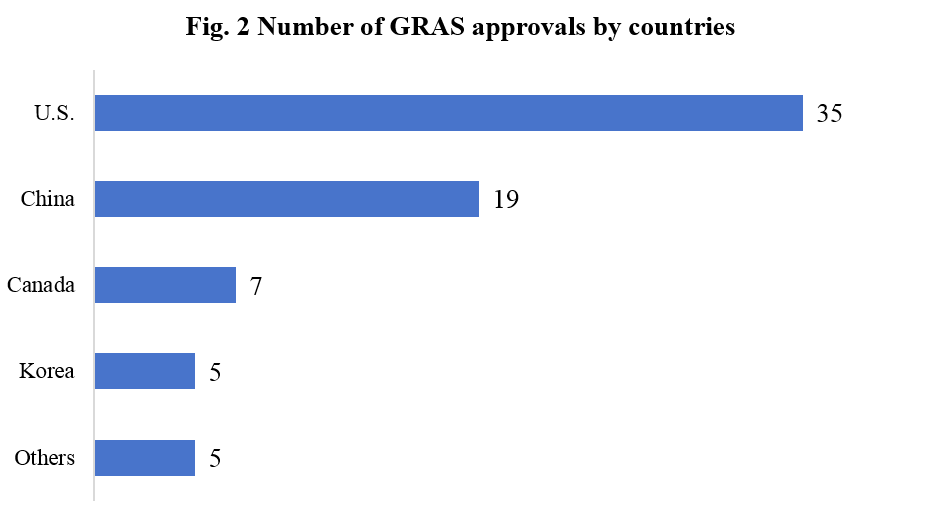
According to publicly available information, applicants for steviol glycosides and rebaudioside are from the United States, China, Canada, South Korea, Japan, Thailand, the Netherlands, and Chile. The number of applicants in China and the United States far exceeds those of other countries, as shown in Figure 2.
Number of approvals by year
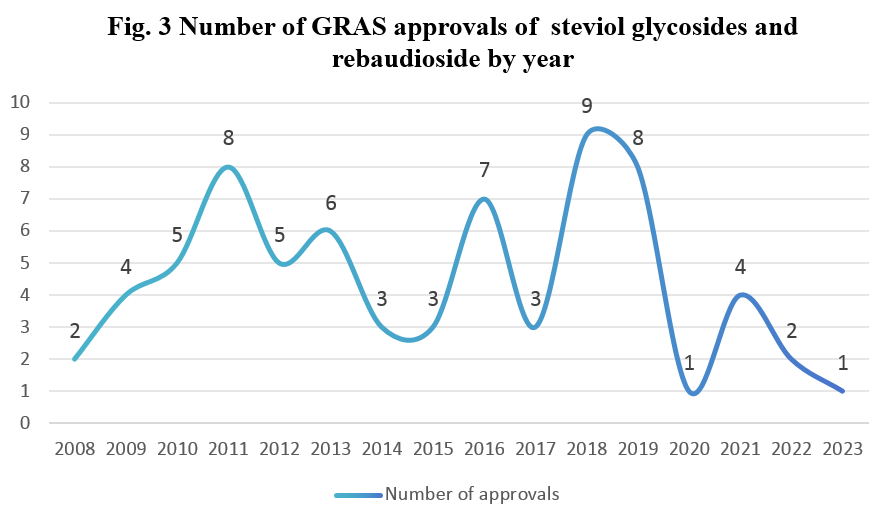
The number of applications for steviol glycosides and rebaudioside peaked in 2011 and 2018 respectively, as indicated in Fig. 3. Around 2011, the applications focused predominantly on steviol glycosides and rebaudioside A. Between 2011 and 2018, the production process of steviol glycosides and its monomers underwent upgrades to align with the market demand, resulting in a wider range of applications. Around 2018, there was a notable shift in application focus towards steviol glycosides and rebaudioside produced through enzymatic treatment and fermentation process.
Trends in the production process
The production process of GRAS-approved steviol glycosides and rebaudiosides mainly falls into three categories, namely purification from the leaves of stevia, enzymatic treatment (mainly involving genetically modified microorganisms), and fermentation process (using genetically modified microorganisms). Based on the data below (see Table 1), it’s evident that with the growing differentiation in the sweetener market demands, the focus in applications is shifting towards specific glycosides. Additionally, the production processes are gradually transitioning from simple plant extraction methods towards synthetic biology technologies capable of producing specific glycosides.
Table 1: List of GRAS certification of steviol glycosides and rebaudiosides
S.N. | Substance | Production process | Acceptance No. /Date | Applicant |
1 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 252 / 2008.12.17 | Whole Earth Sweetener Company LLC - U.S. |
| 2 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 253 / 2008.12.17 | Cargill, Inc. - U.S. |
| 3 | Purified steviol glycosides with rebaudioside A as the principal component | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 275 / 2009.6.11 | McNeil Nutritionals, LLC - U.S. |
| 4 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 278 / 2009.7.20 | Blue California - U.S. |
| 5 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 282 / 2009.8.11 | Sweet Green Fields, LLC - U.S. |
| 6 | Purified steviol glycosides with rebaudioside A and stevioside as the principal components | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 287 / 2009.8.28 | Wisdom Natural Brands - U.S. |
| 7 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 303 / 2010.3.22 | Sunwin USA, LLC & WILD Flavors - U.S. |
| 8 | Purified steviol glycosides with rebaudioside A and stevioside as the principal components | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 304 / 2010.3.22 | Sunwin USA, LLC & WILD Flavors - U.S. |
| 9 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 318 / 2010.5.15 | Pyure Brands, LLC - U.S. |
10 | Purified steviol glycosides with rebaudioside A and stevioside as the principal components | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 323 / 2010.7.9 | PureCircle USA, Inc. - U.S. |
| 11 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 329 / 2010.9.10 | GLG Life Tech, Ltd. - Canada |
| 12 | Enzyme-modified steviol glycosides preparation | Enzymatic treatment | GRN No. 337 / 2011.6.17 | NOW Foods - U.S. |
| 13 | Purified steviol glycosides with rebaudioside A and stevioside as the principal components | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 349 / 2011.7.14 | GLG Life Tech, Ltd. - Canada |
| 14 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 354 / 2011.7.15 | Guilin Layn Natural Ingredients, Corp. - China |
| 15 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 365 / 2011.8.18 | BrazTek International Inc. - U.S. |
| 16 | Purified steviol glycosides with rebaudioside A and stevioside as the principal components | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 367 / 2011.7.8 | Sinochem Health Company, Ltd. - China |
| 17 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 369 / 2011.10.11 | Zhucheng Haotian Pharm Co., Ltd. & Shanghai Freemen Americas, LLC - China |
| 18 | Enzyme-modified steviol glycosides preparation | Enzymatic treatment | GRN No. 375 / 2011.9.2 | Toyo Sugar Refining Co., Ltd. & Nippon Paper Chemicals Co., Ltd. - Japan |
| 19 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 380 / 2011.11.28 | GLG Life Tech Corporation - Canada |
| 20 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 388 / 2012.1.9 | Chengdu Wagott Pharmaceutical - China |
| 21 | Steviol glycosides with stevioside as the principal component | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 389 / 2012.1.18 | Chengdu Wagott Pharmaceutical - China |
| 22 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 393 / 2012.1.23 | Daepyung Co., Ltd. - Korea |
| 23 | Steviol glycosides with rebaudioside A and stevioside as the principal components | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 395 / 2012.1.24 | Daepyung Co., Ltd. - Korea |
| 24 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 418 / 2012.6.7 | MiniStar International, Inc. - U.S. |
| 25 | Enzyme-modified steviol glycosides preparation | Enzymatic treatment | GRN No.448 / 2013.5.3 | Daepyung Co., Ltd. - Korea |
| 26 | Enzyme-modified steviol glycosides | Enzymatic treatment (GMO: Bacillus licheniformis) | GRN No.452 / 2013.7.1 | Daepyung Co., Ltd. - Korea |
| 27 | Rebaudioside D | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 456 / 2013.7.1 | PureCircle USA, Inc. - U.S. |
| 28 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 461 / 2013.8.14 | Almendra Limited - Thailand |
| 29 | Rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 467 / 2013.11.25 | Qufu Xiangzhou Stevia Products Co., Ltd. - China |
| 30 | Purified steviol glycosides with rebaudioside X as the principal component | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 473 / 2013.12.17 | PureCircle, Ltd. - U.S. |
| 31 | High-purity steviol glycosides (minimum purity 95%) | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No.493 / 2014.5.30 | GLG Life Tech Corporation - Canada |
| 32 | Rebaudioside M | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 512 / 2014.10.24 | GLG Life Tech Corporation - U.S. |
| 33 | Rebaudioside C | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 536 / 2015.2.12 | GLG Life Tech Corporation - Canada |
| 34 | Rebaudioside D | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 548 / 2015.4.22 | GLG Life Tech Corporation - Canada |
| 35 | Steviol glycosides with rebaudioside A and stevioside as the principal components | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 516 / 2014.10.31 | Almenda (Thailand) Limited - Thailand |
| 36 | Purified steviol glycosides with rebaudioside A as the principal component | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 555 / 2015.4.21 | Procuctora Alysa SpA - Chile |
| 37 | Glucosylated steviol glycosides | Enzymatic treatment (Bacillus stearothermophilus) | GRN No.607 / 2016.10.14 | PureCircle Limited - U.S. |
| 38 | Purified steviol glycosides | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No.619 / 2016.5.27 | PureCircle Limited - U.S. |
| 39 | Steviol glycosides produced in Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Fermentation process (GMO: Saccharomyces cerevisiae) | GRN No.626 / 2016.5.27 | Cargill, Inc. - U.S. |
| 40 | Rebaudioside A | Fermentation process (GMO: Yarrowia lipolytica) | GRN No. 632 / 2016.6.24 | DSM Nutritional Products, LLC - U.S. |
| 41 | High-purity steviol glycosides (minimum purity 97%) consisting primarily of rebaudioside A | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No. 638 / 2016.7.10 | Hunan Huacheng Biotech Inc. - China |
| 42 | Enzyme-modified steviol glycosides | Enzymatic treatment | GRN No.656 / 2016.9.28 | GLG Life Tech Corporation - U.S. |
| 43 | Glucosylated steviol glycosides (minimum purity 95%) | Enzymatic treatment | GRN No.662 / 2016.9.29 | PureCircle USA - U.S. |
| 44 | Rebaudioside M | Fermentation process (GMO: Saccharomyces) | GRN No. 667 / 2017.2.17 | Blue California - U.S. |
| 45 | Purified steviol glycosides | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No.702 / 2017.9.28 | Xinghua GL Stevia Co., Ltd. - China |
| 46 | Rebaudioside D | Fermentation process (GMO: Saccharomyces) | GRN No. 715 / 2017.10.24 | Blue California - U.S. |
| 47 | Purified steviol glycosides | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No.733 / 2018.1.9 | Shangdong Shengxiangyuan Biotechnology - China |
| 48 | Steviol glycosides consisting primarily of rebaudioside M | Fermentation process (GMO: Brewer’s yeast) | GRN No. 744 / 2018.3.23 | PureCircle Limited - U.S. |
| 49 | Steviol glycosides consisting primarily of rebaudioside M | Enzymatic treatment (GMO: E. coli) | GRN No. 745 / 2018.4.20 | PureCircle Limited - U.S. |
| 50 | Steviol glycosides consisting primarily of rebaudioside M | Fermentation process (GMO: Yarrowia lipolytica) | GRN No. 759 / 2018.5.25 | DSM Food Specialties / DSM Nutritional Products North America - Netherlands |
| 51 | Rebaudioside D | Enzymatic treatment (GMO: Pichia pastoris) | GRN No. 764 / 2018.7.10 | Sichuan Ingia Biosynthetic Co., Ltd. - China |
| 52 | Rebaudioside M | Enzymatic treatment (GMO: E. coli) | GRN No. 780 / 2018.7.31 | Tate and Lyle - U.S. |
| 53 | Steviol glycosides (minimum purity 95%) | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No.790 / 2019.2.26 | GLG Life Tech Corporation - U.S. |
| 54 | Purified steviol glycosides | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No.795 / 2018.9.25 | Steviana Bioscience (Suzhou) Inc. - China |
| 55 | Rebaudioside M | Enzymatic treatment (GMO: Pichia pastoris) | GRN No. 799 / 2018.9.25 | Sichuan Ingia Biosynthetic Co., Ltd. - China |
| 56 | Rebaudioside M | Fermentation process (GMO: Brewer’s yeast) | GRN No.812 / 2018.12.8 | Amyris, Inc. - U.S. |
| 57 | Glucosylated steviol glycosides | Enzymatic treatment (non-genetically modified) | GRN No.821 / 2019.5.7 | Haigen-BGG Natural Ingredients Limited - China |
| 58 | Rebaudioside E | Fermentation process (GMO: Pichia pastoris) | GRN No.823 / 2019.6.21 | Blue California - U.S. |
| 59 | Purified steviol glycosides | Enzymatic treatment | GRN No.838 / 2019.7.12 | Jiang Su Svetia Biotechnology Co., Ltd. - China |
| 60 | Purified steviol glycosides | Enzymatic treatment | GRN No.839 / 2019.7.8 | Sinochem Health Company Ltd. - China |
| 61 | Rebaudioside M | Enzymatic treatment (GMO: E. coli) | GRN No.846 / 2019.8.23 | GLG Life Tech Corporation - Canada |
| 62 | Glucosylated steviol glycosides | Enzymatic treatment | GRN No.858 / 2019.10.4 | Qufu Shengren Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd - China |
| 63 | Glucosylated steviol glycosides | Enzymatic treatment (GMO: Bacillus licheniformis ) | GRN No.878 / 2019.12.19 | Daepyung Co., Ltd. - Korea |
| 64 | Rebaudioside M (genetically modified microorganisms synthesis) | Fermentation process (GMO: Yarrowia lipolytica) | GRN No.882 / 2020.2.2 | Cargill, Inc. - U.S. |
| 65 | Rebaudioside I | Fermentation process (GMO: Pichia pastoris) | GRN No.911 / 2021.6.8 | Blue California - U.S. |
| 66 | Rebaudioside B | Fermentation process (GMO: Pichia pastoris) | GRN No.968 / 2022.3.10 | Blue California - U.S. |
| 67 | Enzyme-modified steviol glycosides | Enzymatic treatment (GMO: Bacillus licheniformis ) | GRN No.970 / 2021.4.9 | Shandong Shengxiangyuan Biotechnology Co., Ltd - China |
| 68 | Purified steviol glycosides from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni) | Purified from the leaves of Stevia rebaudiana | GRN No.983 / 2021.6.28 | Zhucheng Haotian Pharm Co., Ltd - China |
| 69 | Enzyme-modified steviol glycosides | Enzymatic treatment | GRN No.999 / 2021.12.3 | Zhucheng Haotian Pharm Co., Ltd - China |
| 70 | Rebaudioside M | Enzymatic treatment (GMO: E. coli) | GRN No.1010/ 2022.1.26 | Manus Bio, Inc. - U.S. |
| 71 | Rebaudioside I | Enzymatic treatment (GMO: E. coli) | GRN No.1106/ 2023.1.16 | Manus Bio, Inc. - U.S. |
/ | Enzyme-modified steviol glycosides | / | GRN No.1140 / Pending | Tate & Lyle - U.S. |
China
As of now, the compliance process for stevia and its various extracts has begun in China. Detailed application and approval information is shown in the Table below.
Table 2: Regulatory status of stevia and its extracts in China - approved substances
Substance | Function |
Stevia rebaudiana oil | Food additive - food flavoring |
Steviol glycosides | Food additive-sweetener; available excipient for health food filing products |
Glucosylated steviol glycosides | Food additive - food flavoring |
Table 3: Regulatory status of stevia and its extracts in China - accepted substances
Substance | Type of application | Acceptance code | Date of acceptance | Status |
Rebaudioside A | New food additive | 卫食添新申字 (2022)第0004号 | 2022.2.11 | 2022.8.16 Issued for a disapproval decision* |
Stevia | New food additive | 卫食添新申字 (2022)第0005号 | 2022.2.11 | 2022.8.16 Issued for a disapproval decision* |
Stevia extract | New food additive | 卫食添新申字 (2022)第0006号 | 2022.2.11 | 2022.8.1 Issued for a disapproval decision* |
Rebaudioside M | New food raw material | 卫食添新申字 (2023)第0030号 | 2023.3.6 | |
Stevia | New food raw material | 卫食新申字 (2023)第0008号 | 2023.7.9 | / |
Stevia extract | New food raw material | 卫食新申字 (2023)第0015号 | 2023.9.7 | |
Rebaudioside M | New food raw material | 卫食添新申字 (2023)第0034号 | 2023.5.10 | 2023.10.26 |
* Disapproved ≠ not allowed to resubmit. In most cases, based on the results of the technical review, the applicant can refine the materials and then resubmit.
In light of the relevant provisions regarding the application for “Three New Foods” in China, the feasibility and difficulty of applying for one substance is, to some extent, influenced by its international application and approval status. If an enterprise intends to apply for one substance as a new food raw material or new food additive in China, obtaining FDA GRAS certification in the United States or approval as a novel food or food additive in the EU can serve as favorable grounds for the application.
The Food Division at CIRS Group boasts a highly professional team specializing in the application of “Three New Foods” in China, namely new food raw materials, new food additives, and food contact materials, as well as FDA GRAS in the United States and Novel Food in the EU. With extensive experience in these fields, our team has numerous successful cases. As of now, CIRS Group has acted as an agent for dozens of domestic and international applications for new materials and additives involving genetically modified microorganisms, positioning our project experience at the forefront of the industry. We welcome inquiries or visits for a deeper understanding of our technical capabilities.
Note: The data presented is accurate as of December 25, 2023. The information is sourced from publicly available platforms and is for reference only.
If you need any assistance or have any questions, please get in touch with us via service@cirs-group.com.

