On October 7, the National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China (NHC) issued an announcement (No. 8 of 2023) on the approval of 15 “Three New Foods”, including four new food raw materials, six new food additives, and five food-related products. Details are as follows:
New food raw materials (four types)
1. Peach gum
Name | Peach gum | |
Basic information | Source: Prunus persica (L.) Batsch | |
Brief introduction of the production process | Prepared through picking, sorting, airing, cleaning, drying, and other processes by using the gum secreted from Prunus persica (L.) Batsch. | |
Recommended intake | ≤30 grams per day (g/day) | |
Quality requirements | Crude polysaccharide, grams per 100g (g/100 g) | ≥ 60 |
Moisture, g/100 g | ≤ 15 | |
Ash, g/100 g | ≤ 2 | |
Other information |
| |
Lead (Pb), milligrams per kilogram (mg/kg) | ≤ 0.5 | |
Arsenic (As), mg/kg | ≤ 0.5 | |
Ochratoxin A, μg/kg | ≤ 5.0 | |
Coliforms, CFU/g | ≤ 100 | |
Mould and Yeast, CFU/g | ≤ 150 | |
Staphylococcus aureus, /25g | 0 | |
Salmonella, /25g | 0 | |
2. Tiger nut
Name | Tiger nut |
Basic information | Source: Cyperus esculentus L. var. sativus Boeck. Edible part: stem tubers |
Other information | Food safety indicators shall comply with the current national food safety standard for nuts and seeds. |
3. Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. cremoris
Name | Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. cremoris | |
Other information |
| |
Pb, (on dry basis), mg/kg | ≤ 1.0 | |
As, (on dry basis), mg/kg | ≤ 1.5 | |
Salmonella, /25g (mL) | 0 | |
Staphylococcus aureus, /25g (mL) | 0 | |
Listeria monocytogenes, /25g (mL) | 0 | |
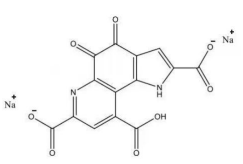
4. Pyrroloquinoline quinone disodium (PQQ) salt
Name | Pyrroloquinoline quinone disodium (PQQ) salt | |
Basic information | CAS: 122628-50-6 Molecular formula: C14H4N2Na2O8 Structure:
Molecular weight: 374.17 | |
Brief introduction of the production process | Prepared through fermentation, extraction, purification, crystallization, drying, and other processes by using Methylovorus glucosotrophus as the production strain. | |
Recommended intake | ≤20 mg/day | |
Quality requirements | Property: | Reddish brown powder |
Pyrroloquinoline quinone disodium (PQQ) salt content (on dry basis), g/100 g | ≥ 98.0 | |
Moisture, g/100 g | ≤ 12.0 | |
Other information |
| |
Pb, mg/kg | ≤ 0.5 | |
As, mg/kg | ≤ 1.0 | |
Cd, mg/kg | ≤ 0.1 | |
Hg, mg/kg | ≤ 0.1 | |
Total plate count, CFU/g | ≤ 1000 | |
Coliforms, MPN/g | ≤ 3.0 | |
Mould and Yeast, CFU/g | ≤ 100 | |
Staphylococcus aureus, /25g | 0 | |
Salmonella, /25g | 0 | |
New food additives (six types)
1. New food enzyme (one type)
No. | Enzyme | Source | Donor |
1 | Serine protease | Bacillus licheniformis | Nocardiopsis prasina |
* The quality specifications of the enzyme shall meet the requirements in the National Food Safety Standard - Food Additives, Enzymes (GB 1886.174).
2. New food nutrition enhancers (three types)
(1) Name: Magnesium lactate
Application scope and maximum usage level: It shall be consistent with the requirements of magnesium in the National Food Safety Standard – Standard for the Use of Food Nutrition Enhancer (GB 14880).
Quality specifications: Applicable to the new food nutrition enhancer magnesium lactate, which is prepared through the reaction of lactic acid and magnesium oxide (or magnesium carbonate).
(2) Name: 2’-fucosyllactose, 2’-FL
Application scope and maximum usage level:
Category number | Food name/category | Usage level | Note |
01.03.02 | Modified milk powder (limited to milk powder for children) | 0.7-2.4 g/L (Count as the state of ready to eat, for powdery products, the level of use should be increased by times of brewing) | When mixed with Lacto-N-neotetraose (LNnT), oligo-galactose, oligofructose, polyfructose and raffinose, the total amount of 2'-fucosyllactose must not exceed 64.5 (g/kg). |
13.01.01 | Infant formula foods | ||
13.01.02 | Older infants and young children formula foods | ||
13.01.03 | Infant formula foods for special medical purposes |
Quality specifications: Applicable to the new food nutrition enhancer 2’-fucosyllactose (2’-FL), which is prepared through fermentation, purification, drying, and other processes using lactose as a raw material. The production strain of 2’-FL should undergo a safety assessment and comply with the requirements outlined in Appendix C.
Appendix C Information on the production strain of 2’-fucosyllactose
Nutrition enhancer | Source | Donor |
2’-fucosyllactose | Coli K12 DH1 MDO | (Helicobacter spp.)a |
E. coli K-12 MG1655 | (Helicobacter spp.)a | |
E. coli BL21 (DE3) | (Neisseria spp.)a |
a is the donor of α-1, 2-fucosyltransferase
(3) Name: Lacto-N-neotetraose, LNnT
Application scope and maximum usage level:
Category number | Food name/category | Usage level | Note |
01.03.02 | Modified milk powder (limited to milk powder for children) | 0.2-0.6 g/L (Count as the state of ready to eat, for powdery products, the level of use should be increased by times of brewing) | When mixed with 2’-fucosyllactose, oligo-galactose, oligofructose, polyfructose and raffinose, the total amount must not exceed 64.5 (g/kg). |
13.01.01 | Infant formula foods | ||
13.01.02 | Older infants and young children formula foods | ||
13.01.03 | Infant formula foods for special medical purposes |
Quality specifications: Applicable to the new nutrition enhancer Lacto-N-neotetraose (LNnT), which is prepared through fermentation, purification, drying, and other processes using lactose as a raw material. The production strain of LNnT should undergo a safety assessment and comply with the requirements outlined in Appendix D.
Appendix D Information on the production strain of Lacto-N-neotetraose
Nutrition enhancer | Source | Donor |
Lacto-N-neotetraose | E. coli K-12 DH1 MDO | (Neisseria spp.)a and (Helicobacter spp.)b |
a is the donor of β-1,3-N-acetylglucosamine transferase
b is the donor of β-1,4-galactosyltransferase
3. New food additives with expanded scope (two types)
No. | Name | Function | Category number | Food name/category | Maximum level (g/kg) | Note |
1 | Calcium lactate | Stabilizer and coagulant, acidity regulator | 04.02.02.03 | Pickled vegetables | 10.0 | - |
04.02.02.04 | Canned vegetables | 3.0 | ||||
2 | Sanzan gum | Thickener, stabilizer, and coagulant | 01.01.03 | Modified milk | 0.5 | - |
14.03.03 | Mixed protein drinks | 0.75 | Count as the state of ready-to-drink, increase the usage of solid drinks according to the dilution ratio. | |||
14.08 | Flavored drinks | 0.5 |
New food-related products (five types)
1. Food contact additives with expanded scope (three types)
No. | Name | CAS number | Application scope | Maximum level (%) |
1 | C.I. pigment black 7; Carbon black | 1333-86-4 | Plastic: PEEK | 0.5 |
2 | Copolymer of acrylamide with methacryloyloxyethyltrimethylammonium chloride, itaconic acid, and N, N '- methylene bisacrylamide | 214495-32-6 | Paper and paperboard | 1.5 (Count as the dry weight) |
3 | 2- (Vinyloxy) -1,2,3-propanecarboxylic acid tributylester | 77-90-7 | Ink with indirect contact with food | 10 |
2. New food contact resin (two types)
No. | Name | CAS number | Range of application | Maximum level (%) |
1 | 1,4-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, polymer with sebacic acid and 1,2-ethanediol | 25067-21-4 | Coating and coating film | Appropriate level |
2 | Polymers of methacrylic acid with butyl methacrylate, ethyl acrylate and methyl methacrylate, and polymers of hydroquinone with 4,4-methylenebis (2,6-dimethylphenol) and chloromethylepoxyethane with N, N-dimethylethanolamine | - | Coating and coating film | 20 (Count as the coating formula) |
If you need any assistance or have any questions, please get in touch with us via service@cirs-group.com.
Further Information